Courtesy of EarthSky
A Clear Voice for Science
www.EarthSky.org
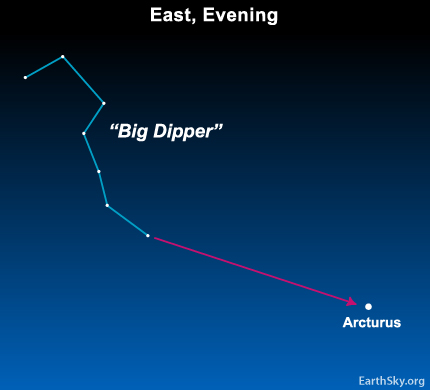
 It is now the perfect time to look outside in the evening and learn a phrase useful to sky watchers. The phrase is: ‘follow the arc to Arcturus.’
It is now the perfect time to look outside in the evening and learn a phrase useful to sky watchers. The phrase is: ‘follow the arc to Arcturus.’
First, locate the Big Dipper asterism in the northeastern sky. Then draw an imaginary line following the curve in the Dipper’s handle until you come to a bright orange star. This star is Arcturus in the constellation Bootes, known in sky lore as the ‘bear guard.’
Arcturus is a giant star with an estimated distance of 37 light-years. It is special because it is not moving with the general stream of stars, in the flat disk of the Milky Way galaxy. Instead, Arcturus is cutting perpendicularly through the galaxy’s disk at a tremendous rate of speed . . . some 150 kilometers per second. Millions of years from now this star will be lost from the view of any future inhabitants of Earth, or at least those who are earthbound and looking with the eye alone.
So that is how to ‘follow the arc’ to the star Arcturus in the constellation Bootes. Learn how you can ‘drive a spike to the star Spica in the constellation Virgo with the help of tomorrow’s sky chart.
Written by Deborah Byrd
Astronomy Picture of the Day from NASA/JPL
U.S. Naval Observator Astronomical Information center
The York County Astronomical Society